이 글은
2023.01.22 - [금융공학] - 워스트포퍼머의 기댓값
워스트포퍼머의 기댓값
이번 글은 2023.01.21 - [금융공학] - 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #3 (Python Code) 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #3 (Python Code) 이번 글은 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #1 2Star WorstPer
sine-qua-none.tistory.com
에서 이어집니다.
저번 글에서는 WorstPerformer의 기댓값을 구하는 Closed form을 유도했습니다.
이제 코드를 통하여 Closed form과 MC 시뮬레이션의 가격을 크로스체크해 보도록 하겠습니다.
코드의 기본 얼개는
2023.01.21 - [금융공학] - 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #3 (Python Code)
2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #3 (Python Code)
이번 글은 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #1 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #2 에서 살펴보았던 2Star WorstPerform Put option을 직접 코딩해 본 결과를 소개하는 글입니다. 먼저 Closed form을
sine-qua-none.tistory.com
에서 소개한 코드와 거의 흡사합니다. 감상해보죠.
Python Code
# 만기시 WorstPerform의 기댓값을 구하는 함수
# 현재가로 환산하려면 discountfactor exp(-r*T)를 곱해주면 됨
def TwoStarWorstPerform_Expectation(objUnderlyings: Underlying, objMarket: Market, maturity, n_iteration, cal_type):
nUnderlying = 2
spot = []
refprice = []
vol = []
div = []
drift = []
diffusion = []
rfr = objMarket._rfr
corr = objMarket._correl
if cal_type == 'MC': # 산출방법 MC simulation
for i in range(nUnderlying):
spot.append(objUnderlyings[i]._spot)
refprice.append(objUnderlyings[i]._refprice)
vol.append(objUnderlyings[i]._volatility)
div.append(objUnderlyings[i]._dividend)
drift.append((rfr - div[i] - 0.5 * vol[i] ** 2) * maturity)
diffusion.append((vol[i] * np.sqrt(maturity)))
spot = np.array(spot)
refprice = np.array(refprice)
drift = np.array(drift)
diffusion = np.array(diffusion)
norm_rand = np.random.normal(size=(n_iteration, 2))
norm_rand_correlated = norm_rand
norm_rand_correlated[:, 1] = corr * norm_rand[:, 0] + np.sqrt(1 - corr ** 2) * norm_rand[:, 1]
mat_price = spot / refprice * np.exp(drift + diffusion * norm_rand_correlated)
worst_perf = np.min(mat_price, axis=1) # worst performer 를 n_iteration만큼 산출
worst_perf_expectation = worst_perf.mean() # worst performer의 기댓값
return worst_perf_expectation
elif cal_type == 'CF': # 산출방법 CF :Closed Form
corrMatrix = np.array([[1, corr], [corr, 1]])
for i in range(nUnderlying):
spot.append(objUnderlyings[i]._spot)
refprice.append(objUnderlyings[i]._refprice)
vol.append(objUnderlyings[i]._volatility)
div.append(objUnderlyings[i]._dividend)
drift.append((rfr - div[i] - 0.5 * vol[i] ** 2) * maturity)
diffusion.append((vol[i] * np.sqrt(maturity)))
spot = np.array(spot)
refprice = np.array(refprice)
vol = np.array(vol)
div = np.array(div)
drift = np.array(drift)
diffusion = np.array(diffusion)
eta = np.log(spot / refprice) + drift
p0 = np.array([np.inf, eta[1] - eta[0]]) # numpy.inf는 무한대를 뜻함
p1 = np.array([eta[0] - eta[1], np.inf])
points = np.array([p0, p1])
lambda0 = np.array([[diffusion[0], 0], [diffusion[0], -diffusion[1]]])
lambda1 = np.array([[-diffusion[0], diffusion[1]], [0, diffusion[1]]])
dMatrix0 = lambda0 @ corrMatrix @ lambda0.transpose()
dMatrix1 = lambda1 @ corrMatrix @ lambda1.transpose()
dMatrix = np.array([dMatrix0, dMatrix1])
e0 = np.array([1, 0]).transpose()
e1 = np.array([0, 1]).transpose()
elementVec = np.array([e0, e1])
value = np.zeros(2)
for i in range(nUnderlying):
dist = mvn(mean=dMatrix[i] @ elementVec[i], cov=dMatrix[i])
value[i] = spot[i] / refprice[i] * np.exp(
drift[i] + 0.5 * elementVec[i].transpose() @ dMatrix[i] @ elementVec[i]) * dist.cdf(points[i])
return (value[0] + value[1])
else:
return -999
○ numpy.inf 는 무한대를 뜻합니다. 자세한 내용은 관련 tutorial를 보시기 바랍니다.
이제 다음의 코드를 실행해 보겠습니다. 두 기초자산의 변동성은 30%로 동일하고 연속배당률이 없으며 만기 1인 워스트 포퍼머의 기댓값입니다.
두 기초자산의 현재가의 수준(100)과 비교하기 위해 discount factor를 곱해 현재가로 할인했습니다.
if __name__ == '__main__':
rfr = 0.03
maturity = 1
wp_val_cf_list = []
wp_val_mc_list = []
spot_vec = np.arange(50, 150 + 10, 10)
market = Market(rfr=rfr, correlation=- 0.9999) # correlation을 -1로 둠
for spot in spot_vec:
two_assets = []
# 기초자산의 현재가, 기준가, 변동성을 각각 100, 100, 30%로 동일시함
underlying_spot1 = Underlying(refprice=100, spotvalue=spot, volatility=0.3, dividend=0)
underlying_spot2 = Underlying(refprice=100, spotvalue=spot, volatility=0.3, dividend=0.0)
two_assets.append(underlying_spot1)
two_assets.append(underlying_spot2)
# closed form과 mc가격 둘다 계산
wp_val_cf = TwoStarWorstPerform_Expectation(objUnderlyings=two_assets, objMarket=market, maturity=maturity,
n_iteration=10000, cal_type='CF')
wp_val_mc = TwoStarWorstPerform_Expectation(objUnderlyings=two_assets, objMarket=market, maturity=maturity,
n_iteration=10000, cal_type='MC')
wp_val_cf_list.append(wp_val_cf)
wp_val_mc_list.append(wp_val_mc)
#할인율을 곱하여 worstperformer의 현재기댓값을 구함
discountfactor = np.exp(-rfr * maturity)
wp_val_cf_list = discountfactor * np.array(wp_val_cf_list)
wp_val_mc_list = discountfactor * np.array(wp_val_mc_list)
plt.plot(spot_vec, wp_val_cf_list, marker='o', label='WorstPerform Expectation(Closedform)')
plt.plot(spot_vec, wp_val_mc_list, label='WorstPerform Expectation(MC)')
plt.xlabel('stock')
plt.legend()
# plotting에 주석을 달기위한(annotate) 함수
for x, y in zip(spot_vec, wp_val_cf_list):
label = '({:.0f}, {:.2f})'.format(x, y) # x, y좌표를 문자열로 만듬.
plt.annotate(label, # 출력할 텍스트, 여기에선 y좌표
(x, y), # 텍스트를 출력할 좌표
textcoords="offset points", # 텍스트 위치를 (x,y)로 부터의 오프셋 (offset_x, offset_y)로 지정
xytext=(0, 5), # (x, y)로 부터의 오프셋 (offset_x, offset_y), 여기에선 y 좌표로 +20 이동합니다.
ha='center') # 수평방향으로 중앙정렬합니다.
plt.show()
print(wp_val_cf_list - wp_val_mc_list)○ plt.annotate 로 그래프에 점의 좌표, 주석 등 글을 쓸 수 있습니다. 자세한 용법은 tutorial을 참고해 보세요.
다음은 결과입니다.
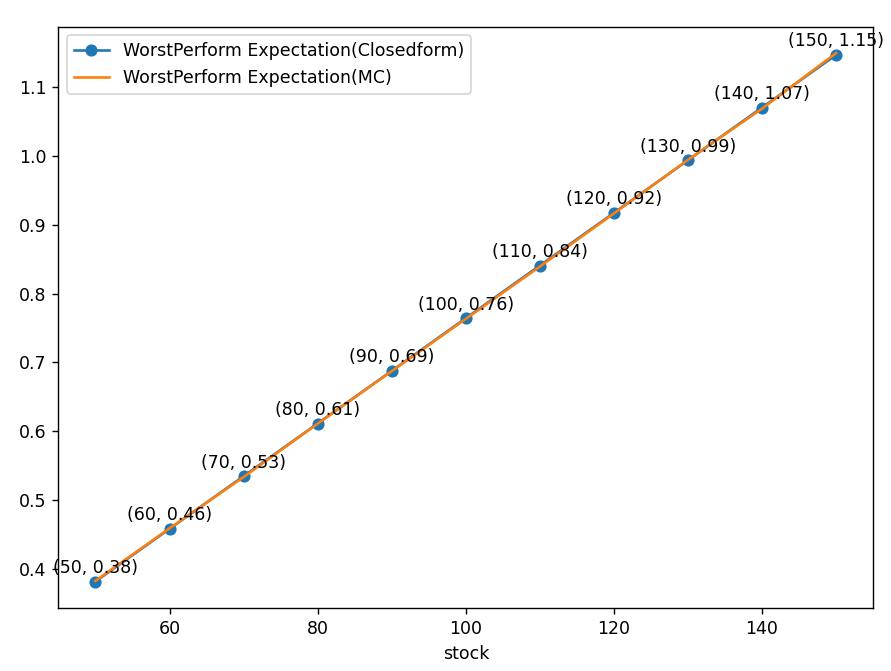
현재가 100인 상환에서 변동성 30%을 가지고 완전 반대로 움직이는(correlation=-1) 두 자산의 워스트포퍼머는 76%수준까지 떨어지는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
다음은 상관계수를 0으로 놓았을 때입니다.
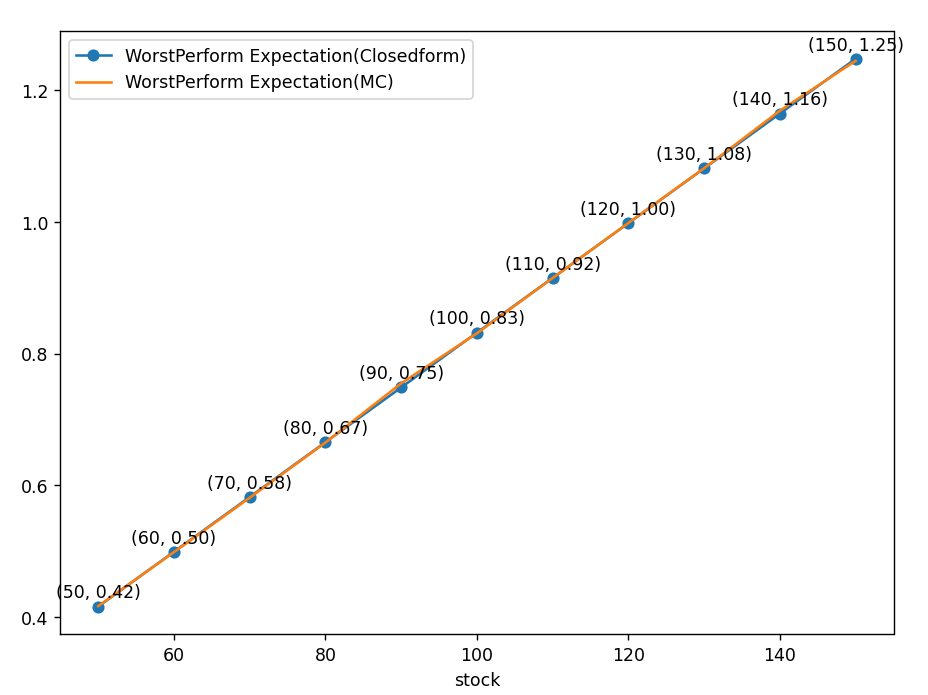
현재가 100인 상환에서 변동성 30%을 가지고 서로 독립적으로 움직이는 두 자산의 워스트포퍼머는 83%수준까지 떨어지는 것을 알 수 있습니다.
마지막으로 상관계수 1일 때입니다. 1을 넣으면 오류가 나므로 0.9999 정도를 넣어봅니다.
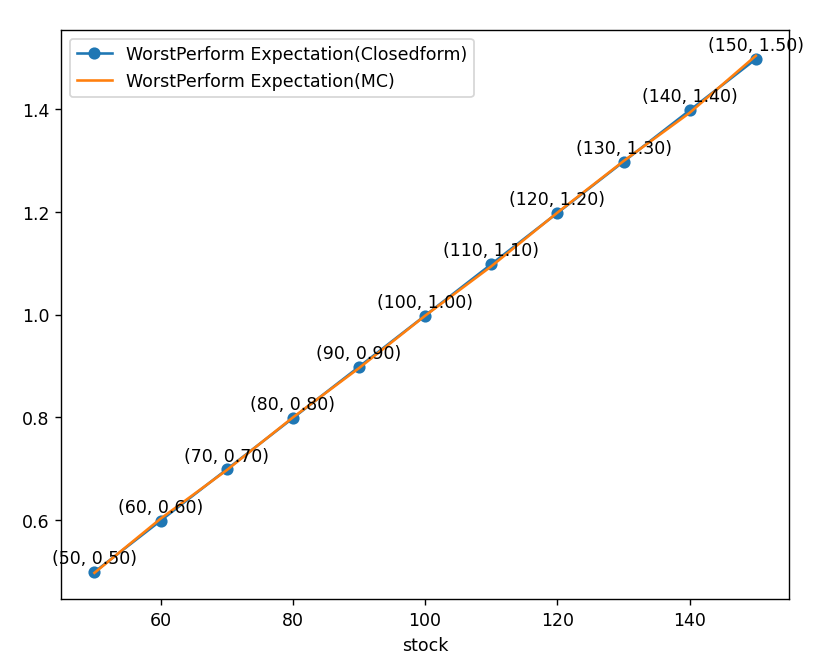
상관계수가 1이라는 얘기는 그냥 하나의 기초자산이라는 뜻이죠. 당연히 현재가와 워스프 포퍼머가 일치합니다.
따라서 워스트 포퍼머의 직관적인 움직임이 공식을 통하여 잘 설명이 되고, 세 그림에서 살펴봤듯이 MC 가격과 Closed form가격이 일치하며, 이를 통해
워스트포퍼머를 기초자산으로 하는 델타원 상품
의 가격도 구할 수 있게 되었습니다.
'금융공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 두드림 ELS? Do Dream? 2X 드림! (0) | 2023.03.14 |
|---|---|
| 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: FDM(OSM) (0) | 2023.02.28 |
| 워스트포퍼머의 기댓값 (0) | 2023.01.22 |
| 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #3 (Python Code) (0) | 2023.01.21 |
| 2Star WorstPerform 풋옵션 가격: Closed form #2 (0) | 2023.01.19 |



댓글